Our reviewers evaluate career opinion pieces independently. Learn how we stay transparent, our methodology, and tell us about anything we missed.

Home › What is Documentation? The… ›
When I first started doing documentation inside product teams, I thought the hard part was writing. It wasn’t. The hard part was getting the right people aligned on what “true” even meant, and then keeping that truth updated while everything changed around it.
If you’ve ever opened a doc that looked polished but gave you the wrong result, you already understand why technical documentation matters. Trust is the whole game.
Technical documentation exists to remove uncertainty. It helps users complete tasks, helps internal teams align on how things work, and helps organizations meet safety, legal, and quality expectations when they apply.
When documentation is done well, it reduces support load, speeds up onboarding, and prevents expensive mistakes. If you want a practical view of how strong docs show up in real products, I like using software documentation examples that set the standard to calibrate what “good” looks like.
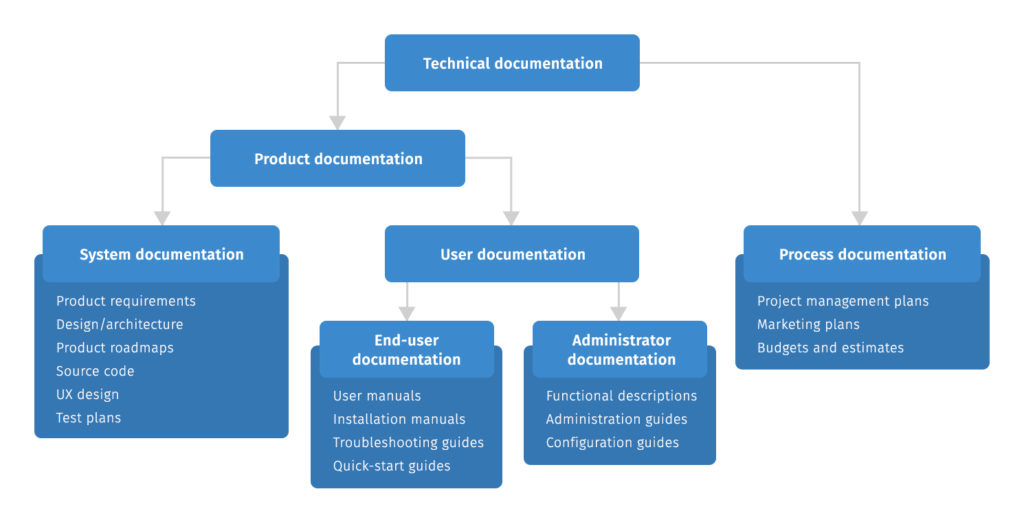
I usually bucket technical documentation into two categories: documentation for using the thing, and documentation for building or operating the thing. Teams label these differently, but the reader’s intent is what stays consistent.
For a deeper breakdown of what counts as “product docs” in the real world, I point people to what product documentation is and how teams use it because it clarifies the boundary between end-user help and internal implementation details.
Here are the doc formats you’ll see most often:
If you’re documenting APIs, the workflow and structure shift a bit. I recommend following how I write API documentation in 6 practical steps to avoid the usual “wall of endpoints” problem.
If you take only one thing from this article, let it be this: technical documentation is not “for everyone.” It’s for a specific target group in a specific moment, trying to accomplish something specific.
Your audience might be developers integrating an API, machine operators running equipment, operating staff following procedures, service technicians diagnosing failures, or test groups validating a new release. Each of those readers has a different context, a different tolerance for detail, and a different definition of success.
This is why I care so much about the information concept behind a doc set. I want each page to answer one primary question for one primary user, instead of trying to be a comprehensive encyclopedia. The moment you try to “cover everything,” the doc becomes harder to scan, harder to maintain, and easier to misinterpret.
Now, stakeholders are a different story. Stakeholders are the people who help you get the doc right and get it shipped at the right time.
Here’s what that typically looks like in a real team:
One practical thing I do is map stakeholders to a simple responsibility grid. I assign who writes, who reviews for accuracy, who reviews for usability, and who signs off. That sounds formal, but it prevents the most common failure I see, which is a doc that gets “reviewed by everyone” and approved by no one.
Want to learn how to create outstanding technical documentation? Check out our technical writing certification course!
Strong technical documentation has the same backbone: a clear goal, prerequisites, steps, expected results, and next actions when something goes wrong. Readers do not want a long narrative. They want a path.
I separate structure from layout as early as possible. Structure is your information architecture, while layout is how the content is presented with headings, visuals, and navigation. Once that separation is clear, it becomes much easier to keep content accurate across variants and versions.
Here’s a lightweight structure I reuse constantly:
If your docs live across multiple releases or product variants, versioning becomes part of the content requirements. That’s where a system that outlines document version control and how teams manage it stops being “process overhead” and starts being sanity.
Let me tell you how I actually approach creating technical documentation, because the “ideal process” and the real process are often two different things.
I start with planning, even when I’m under time pressure. I clarify the audience, the single job-to-be-done, and what success looks like when the reader finishes. If you skip this, you will end up writing a doc that feels complete but fails in real use.
Next, I built the doc around step-by-step instructions that match the reader’s workflow. That means I write steps in the order users actually do them, not the order the system architecture makes sense to me. I also make expected outcomes explicit, because readers need feedback loops to know they’re on track.
Templates help more than most people expect. When the same doc type repeats, a template reduces decision fatigue and makes docs easier to review. It also makes your doc set feel cohesive, which improves trust.
Consistency is the other big lever. I keep a simple editorial guide, even if it’s lightweight, and I align it with the brand style guide when one exists. That includes terminology rules, tone, formatting conventions, and what to do with warnings, notes, and prerequisites.
Review is where teams either win or bleed. I rely on a review process that matches the stakes. For low-risk content, a quick SME check is fine. For higher-risk content, I prefer the four eyes principle, where at least two qualified reviewers verify accuracy and usability.
In practice, Jira and Confluence often become the workflow backbone. Jira is where the work gets tracked and scheduled. Confluence is where drafts live and get reviewed. Even if you do docs-as-code, you still need a clear workflow for who reviews what and when.
Finally, plan for translation earlier than you think you need to. Translation management is smoother when your source content has stable terminology, reusable chunks, and clear metadata. If you wait until the end, you end up rewriting content while it’s already being localized, and that gets expensive fast.
If you want a checklist that’s close to how I operate day-to-day, I often borrow from good documentation practices I use to keep docs clear and maintainable.
Tools matter, but not in the way most people think. The tool will not save weak ownership, vague audiences, or missing reviews. What it can do is make good habits easy and make bad habits harder to hide.
I like thinking about documentation tools in layers. At the base layer, you have where drafts are created. Next, you have how content is reviewed and approved. Then you have how it’s published and maintained, including metadata, modularization, and variant management.
A lot of teams start in Microsoft Word, especially when documentation needs formal formatting, tracked changes, and offline sharing. Word is surprisingly effective for heavily reviewed documents, but it can become painful when you need to reuse content across products or keep many versions aligned.
For collaborative teams, Confluence is one of the most common starting points. It works well as a collaborative platform because multiple stakeholders can review in one place, and it’s easy to connect documentation work to Jira tickets. The tradeoff is long-term consistency, because large Confluence spaces can turn into a messy knowledge dump if you don’t enforce structure.
Tools like Document360 are designed specifically for knowledge bases and help centers. The benefit is a more product-like documentation experience, including search, categorization, and publishing workflows that are built for documentation instead of general wiki content. These platforms often make it easier to keep public docs clean while still supporting internal drafts and approvals.
Once documentation scales, most teams eventually hit the same wall. You cannot keep duplicating the same content in five different places and expect it to stay accurate. This is where a content management system or a component content management system (CCMS) becomes attractive.
A CCMS supports modularization, which means you write content in reusable chunks and assemble it into different outputs. This is the foundation for maintaining consistent warnings, prerequisites, and reference sections across multiple manuals or product variants.
Metadata is the quiet hero here. With good metadata, you can tag content by product, version, audience, region, or feature. That makes it possible to automate publishing rules and reduce manual cleanup. Metadata also supports better search and filtering, which is a big deal when users are trying to find one specific answer under stress.
In more complex environments, especially hardware, manufacturing, and regulated industries, teams often use an XML-based component content management system. The goal is consistency, reuse, and controlled outputs, not casual writing speed.
You’ll see enterprise authoring systems like Schema ST4 in this space. These tools support structured authoring, strong reuse models, and variant management. They also tend to integrate with translation workflows and terminology management, which matters a lot when content is produced across markets and languages.
The tradeoff is that these tools can feel heavy if your team is small or fast-moving. The learning curve is real, and structured authoring only pays off when you commit to the process and standards that make structure meaningful.
Variant management is what you need when one “product” is really ten products with shared components. If you have multiple versions, regional configurations, or customer tiers, variant management lets you publish the right combination of content without copying and pasting.
This is where modularization, metadata, and a CCMS approach come together. You define what varies, what stays consistent, and what rules control the output. When teams do this well, documentation maintenance becomes predictable. When teams do it poorly, they ship contradictory instructions to different customers, and support takes the hit.
If you’re building software documentation specifically, I’ve laid out the end-to-end process for writing software documentation in 7 simple steps. It helps you choose tools based on workflow instead of hype.
Not every team needs formal standards, but when you do, you really do. Regulated industries and safety-critical products often require controlled language, terminology management, and documented review processes.
Two references I see teams lean on a lot are the general principles for instructions for use in IEC/IEEE 82079-1:2019 on ISO’s site and, for machinery, the compliance expectations in the EU’s Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC on EUR-Lex.
Even if you are not formally “doing ISO,” standards and editorial guides are still useful because they force decisions. They push you to define voice, terminology rules, readability requirements, and how approvals work, which is exactly what keeps documentation consistent over time.
The biggest challenge is keeping documentation accurate as products change. Agile methods move fast, and without a clear ownership model, docs become stale. That’s why managing updates is not a maintenance task; it’s a design requirement.
Another common problem is usability. Many docs are technically correct but still unusable because they ignore real user workflows. A quick usability test, even with five people from your target audience, often reveals missing prerequisites, unclear steps, or terminology mismatches.
Finally, time pressure forces shortcuts, and shortcuts compound. When teams skip reviews, translation planning, or terminology consistency checks, they usually pay for it later in support tickets, rework, and trust loss.
If you want to improve your technical documentation quickly, start with audience clarity, a repeatable structure, and a review workflow you can actually sustain. Tools and standards are multipliers, but only after the fundamentals are stable. If you want help building your career around these skills, technical writing skills are a good place to start.
FAQ
Here I answer the most frequently asked questions about technical documentation.
The goal is to help a specific audience complete a task or understand a system with minimal confusion. Good technical documentation makes the correct action feel obvious, and the incorrect action feel hard to do.
Technical writers usually own the structure and quality, but SMEs, developers, and product managers need to validate accuracy and timing. If documentation affects compliance or safety, you often need formal reviewers and a tracked approval process.
User documentation is a subset of technical documentation focused on helping end users operate a product. It’s usually more task-focused and less implementation-heavy than developer-facing documentation.
The best tool is the one your team will maintain consistently. Early teams do fine with a wiki or a knowledge base platform, while scaling teams often move toward docs-as-code or a CMS that supports modularization, metadata, and version control.
Get certified in technical writing skills.